ASTR 1010 FALL 2019:
Practice Problems for Quiz #3
1.
What type of light has wavelengths in between
that of X-rays and visible light?
a) Gamma rays.
b) Infrared.
c) Ultraviolet.
d) Radio.
e) Microwaves.
2. The Earth is 81 times more massive than the Moon.
The center of mass of the Earth/Moon system is therefore:
a) 1/82nd of the way from the Earth to the Moon, closer to the Earth.
b) 1/82nd of the way from the Moon to the Earth, closer to the Moon.
c) 1/9th of the way from the Earth to the Moon, closer to the Earth.
d) 1/9th of the way from the Moon to the Earth, closer to the Moon.
e) exactly half way between the Earth and the Moon.
3.
Light Bulb A has
a yellowish glow,
Light Bulb B has a reddish glow,
and Light Bulb C has a blueish white glow.
Therefore, in order of temperature, from coldest to hottest, the filaments
in the bulbs
are:
a) A, B, C.
b) C, A, B.
c) A, C, B.
d) B, A, C.
e) C, B, A.
4. An astronaut on the International Space Station orbiting Earth:
a) has a mass of 0 kg.
b) does not feel any gravitational force.
c) is not accelerating.
d) is constantly accelerating.
e) has a mass equal to 1/6th of his/her mass on Earth.
5. The temperature that water freezes at is:
a) 0K.
b) -273K.
c) 273K.
d) 373K.
e) 32K.
6. Which of the following is a unit of luminosity (power)?
a) joule.
b) Calorie.
c) m/s2.
d) watt.
e) kilowatt-hour.
7. Which of the following types of light carries the most energy?
a) X-rays.
b) Infrared.
c) Ultraviolet.
d) Gamma rays.
e) Radio waves.
8. An ionized atom is:
a) an atom with an electron that has jumped to a higher
energy level.
b) an atom that has lost an electron.
c) an atom that has bound to another atom to make a molecule.
d) an atom with an extra neutron.
e) an atom with an electron that has jumped to the ground
energy level.
9. The vapor lamps used in class
contain hot, low density gas. They
produce light when:
a) the solid filaments in the lamps are heated, producing
thermal radiation.
b) electrons in the atoms jump up to higher energy levels,
at the same time
emitting photons of light.
c) a source of continuous radiation lies behind a low density
gas. The gas absorbs light at only certain wavelengths, producing
spectral lines.
d) electrons escape from the atoms.
e) collisions between atoms excite the atoms, which
then spontaneously de-excite, producing light at only certain
wavelengths.
10. A 13C atom contains:
a) 6 protons, 13 neutrons.
b) 7 protons, 6 neutrons.
c) 13 protons, 13 neutrons.
d) 13 protons, 0 neutrons.
e) 6 protons, 7 neutrons.
11. What kind of spectrum does the Sun have?
a) a continuous spectrum.
b) an emission-line spectrum.
c) an absorption-line spectrum.
d) only yellow light.
e) only visible light.
12. Star A has a surface temperature of 3000K, while
Star B has a surface temperature of 12,000K.
Therefore the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star A is:
a) Half the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star B.
b) Twice the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star B.
c) Four times the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star B.
d) One quarter the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star B.
e) Sixteen times the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star B.
13. An absorption line
spectrum is produced by:
a) a low density gas.
b) a low density gas in front of a hot solid object or hot dense gas.
c) a hot solid object or hot dense gas.
d) the filament in a light bulb.
e) a vapor lamp, like the neon lamp shown in class.
14. Atom A has 1 proton, 0 neutrons, and 1 electron.
Atom B has 1 proton, 1 neutron, and 1 electrons.
Therefore:
a) Atom A and Atom B are both carbon atoms.
b) Atom A and Atom B are both ions.
c) Atom A and Atom B are isotopes of each other.
d) Atom A is a hydrogen atom; Atom B is a helium atom.
e) Atom A and Atom B have the same mass.
15. In the energy level diagram of a hydrogen atom:
a) the energy levels are all exactly the same distance apart.
b) the energy levels get closer together as one goes to higher energies.
c) the energy levels get further apart as one goes to higher energies.
d) there is only one energy level.
e) there are only two energy levels.
16. A Doppler shift is:
a) A change in the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of an object,
as the temperature of the object changes.
b) A change in the wavelength of the light from an object,
due to the relative motion of the object and the observer.
c) A change in the energy of an electron, when it jumps to a higher
energy level in an atom.
d) The bending of a ray of light as it goes from one medium to another.
e) The emission of a photon of light by an atom, when an electron
in the atom jumps to a lower energy level.
17. Star A has a surface temperature of 5000K, while
Star B has a surface temperature of 10,000K.
Therefore the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star A is:
a) Half that of the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star B.
b) Twice that of the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star B.
c) The same as the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star B.
d) Four times that of the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star B.
e) One quarter that of the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star B.
18.
A 100-watt light bulb uses how much energy in a second?
a) 100 joules.
b) 1 kilowatt-hour.
c) 100 watts.
d) 0.1 kilowatt-hour.
e) 1 kilowatt.
19.
We can see each other in the classroom because:
a) we emit thermal radiation.
b) we emit visible light.
c) we emit infrared light.
d) we reflect visible light.
e) we emit radio waves.
20.
The conversion between degrees Fahrenheit and degrees
Kelvin is:
a) T(K) = 5/9(T(F) - 32) - 273
b) T(K) = 9(T(F) + 32)
c) T(K) = 5/9(T(F) - 32)
d) T(K) = 5/9(T(F) - 273)
e) T(K) = 5/9(T(F) - 32) + 273
21.
Tom weighs 100 lbs and Bob weighs 200 lbs.
They are sitting on the two ends of a board
which is balanced over a log. The distance between
Tom and the log is X(T), while the distance between
Bob and the log is X(B).
How do X(T) and X(B) compare?
a) X(T) = 2 X(B).
b) X(T) = 1/2 X(B).
c) X(T) = X(B).
d) X(T) = 100 X(B).
e) X(T) = 1/100 X(B).
22. What type of light has wavelengths in between
that of gamma rays and ultraviolet light?
a) Visible.
b) Infrared.
c) X-rays.
d) Radio.
e) Microwaves.
23. A continuous spectrum is produced by:
a) a low density gas.
b) a low density gas in front of a hot solid object.
c) a hot solid object or hot dense gas.
d) a low density gas in front of high density gas.
e) a vapor lamp, like the neon lamp shown in class.
24. A frequency of 10 Hertz equals:
a) 10 joules/second.
b) 10 meters/second.
c) 10 wavelengths/second.
d) 10 watts/second.
e) 10 meters/second2.
25. Kinetic energy is:
a) Energy of motion.
b) Stored energy.
c) Energy carried by light.
d) Nuclear energy.
e) Solar energy.
26. Which of the following types of light carry less
energy than visible light?
a) X-rays and ultraviolet light.
b) Infrared and radio waves.
c) Ultraviolet and infrared.
d) Gamma rays, X-rays, and ultraviolet.
e) Radio waves and X-rays.
27. An astronaut in orbit around the Earth in
the Space Shuttle experiences `weightlessness'
because:
a) He or she is so far from the Earth that the gravitational
force due to the Earth is zero.
b) His or her mass is zero.
c) There is no gravity in space.
d) He or she is moving at the escape velocity of Earth.
e) He or she is falling around the Earth.
28.
Ganymede has a mass of about 1/1000th that of Jupiter.
Where is the center of mass of the Jupiter-Ganymede system?
a) About 1/1000th of the way from Jupiter to Ganymede, closer to
Jupiter.
b) About 1/1000th of the way from Jupiter to Ganymede, closer to
Ganymede.
c) halfway between Jupiter and Ganymede.
d) About (1/1000)^2 = 10^-6 of the way from Jupiter to Ganymede,
closer to Jupiter.
e) About (1/1000)^2 = 10^-6 of the way from Jupiter to Ganymede,
farther from Jupiter.
29. A photon of light with a wavelength of 8000 Angstroms has an energy
of:
a) Half that of a photon with a wavelength of 4000 Angstroms.
b) Twice that of a photon with a wavelength of 4000 Angstroms.
c) The same as that of a photon with a wavelength of 4000 Angstroms.
d) Four times that of a photon with a wavelength of 4000 Angstroms.
e) One quarter that of a photon with a wavelength of 4000 Angstroms.
30. Which of the following lists the six regimes
of the electromagnetic spectrum in the correct order, from
shortest wavelength to longest wavelength?
a) Gamma Rays, X-Rays, Infrared, Visible, Ultraviolet, Radio.
b) Gamma Rays, X-Rays, Visible, Ultraviolet, Infrared, Radio.
c) Gamma Rays, UV, Visible, Infrared, X-Rays, Radio.
d) Gamma Rays, X-Rays, UV, Visible, Infrared, Radio.
e) Radio, Infrared, Visible, UV, Gamma Rays, X-Rays.
31. Microwaves are:
a) High energy Gamma Rays.
b) Cosmic Rays.
c) High frequency radio waves.
d) Short wavelength visible light.
e) X-rays.
32.
An interstellar dust grain is very cold, about 100K (-173 deg C).
At what wavelengths does it emit most of its thermal radiation?
a) X-ray.
b) Ultraviolet.
c) Gamma Ray.
d) Infrared.
e) Optical.
33. Zero degrees Kelvin is:
a) the boiling point of water.
b) the freezing point of water.
c) Zero degrees Celsius.
d) the boiling point of nitrogen.
e) absolute zero.
34. Radiative energy is:
a) energy of motion.
b) energy stored for future use.
c) energy from nuclear power plants.
d) energy carried by light.
e) energy used by car radiators.
35. Which of the following is NOT a unit of energy?
a) watt.
b) joule.
c) Calorie.
d) kilowatt-hour.
e) calorie.
36.
What type of light has the longest wavelengths?
a) Gamma rays.
b) Infrared.
c) Ultraviolet.
d) Radio.
e) Microwaves.
37.
The Sun has a yellowish appearance,
Betelgeuse
has a reddish glow,
and Vega has a blueish white glow.
Therefore, the temperature order, from coldest to hottest, is:
a) Vega, the Sun, Betelgeuse.
b) Betelgeuse, Vega, the Sun.
c) The Sun, Vega, Betelgeuse.
d) Betelgeuse, the Sun, Vega.
e) Vega, Betelgeuse, the Sun.
38. An excited atom is:
a) an atom with an electron that has jumped to a higher
energy level.
b) an atom that has lost an electron.
c) an atom that has bound to another atom to make a molecule.
d) an atom with an extra neutron.
e) an atom with an electron that has jumped to the ground
energy level.
39.
A watt is a unit of:
a) energy.
b) luminosity.
c) brightness.
d) frequency.
e) density.
40. The Moon has a surface temperature between 100-400K.
Therefore, its thermal radiation is mainly in:
a) X-rays.
b) the visible.
c) the infrared.
d) gamma rays.
e) the ultraviolet.
41. A spectrum that looks like a rainbow with
some dark lines drawn on it
(i.e., it has all colors except a few specific colors), is produced by:
a) a low density gas.
b) a hot solid object.
c) a hot dense gas.
d) a vapor lamp, like the neon lamp shown in class.
e) a low density gas in front of a hot solid or hot dense gas.
42. Which of the following is a unit of frequency?
a) a joule.
b) a joule/second.
c) a watt.
d) a meter/second2.
e) a Hertz.
43. Which of the following lists the six regimes
of the electromagnetic spectrum in the correct order, from
lowest energy to highest energy?
a) Gamma Rays, X-Rays, Infrared, Visible, Ultraviolet, Radio.
b) Radio, Infrared, Gamma Rays, Visible, Ultraviolet, X-Rays.
c) Radio, Infrared, Visible, Ultraviolet, X-Rays, Gamma Rays.
d) Gamma Rays, X-Rays, UV, Visible, Infrared, Radio.
e) Radio, Infrared, Visible, UV, Gamma Rays, X-Rays.
44. 373 degrees Kelvin is:
a) the boiling point of water.
b) the freezing point of water.
c) Zero degrees Celsius.
d) the boiling point of nitrogen.
e) absolute zero.
45. A low density cloud of interstellar gas, without
a bright source behind it, produces:
a) an emission line spectrum.
b) an absorption line spectrum.
c) a continuous spectrum.
d) only infrared radiation.
e) only blue radiation.
46.
A hot burner on a stove produces:
a) A continuous spectrum.
b) An emission-line spectrum.
c) An absorption-line spectrum.
d) A spectrum similar to that of the Sun.
e) A spectrum that peaks in the ultraviolet part of the
spectrum.
47. The H-alpha line of hydrogen
is observed in Star A at a wavelength
of 6000 Angstroms.
In the laboratory, the wavelength of the H-alpha line is 6563 Angstroms.
This means that:
a) Star A is a blue star.
b) Star A is moving towards us.
c) Star A is moving away from us.
d) Star A is very hot.
e) Star A is very cold.
48. Which of the following types
of light has the
lowest frequency?
a) Gamma rays.
b) Visible light.
c) Radio waves.
d) Infrared light.
e) Ultraviolet light.
49. A Hertz is a:
a) joule/sec.
b) calorie/sec.
c) m/s2.
d) 1/sec.
e) kilowatt-hour.
50. The vapor lamps shown in class
produce:
a) emission line spectra.
b) absorption line spectra.
c) continuous spectra.
d) dark line spectra.
e) blackbody radiation.
51. Star A has a surface temperature 1/3rd that that
of Star B. Therefore,
the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star A is:
a) three times larger than that of Star B.
b) 1/3 that of Star B.
c) nine times larger than that of Star B.
d) 1/9th that of Star B.
e) the same as that of Star B.
52. Which of the following types
of light has the
lowest energy?
a) Gamma rays.
b) Visible light.
c) Radio waves.
d) Infrared light.
e) Ultraviolet light.
53. Which of the following is a unit of energy?
a) Hertz.
b) Watt.
c) m/s2.
d) joule/sec.
e) kilowatt-hour.
54. Which type of light has wavelengths in between those
of radio and those of visible light?
a) ultraviolet.
b) infrared.
c) gamma rays.
d) microwaves.
e) radio.
55. When a scientist says that an
astronaut in a spacecraft
is in a `weightless' state, he/she means that the astronaut:
a) is massless.
b) is in free fall.
c) has zero acceleration.
d) has zero net gravitational force pulling on him/her.
e) is moving at constant velocity.
56. A low density cloud of gas in front of a hot solid object
produces:
a) an emission-line spectrum.
b) an absorption-line spectrum.
c) a continuous spectrum.
d) a thermal spectrum.
e) a bright-line spectrum.
57. The speed of light is 3 X 108 m/s.
Radio waves with a frequency of 300 MHz have a wavelength of:
a) 9 X 1010 meters.
b) 9 X 1016 meters.
c) 106 meters.
d) 1 meter.
e) 9 X 10-6 meters.
58. The temperature of the photosphere of the Sun is
5800K, and the peak of the spectrum of the Sun
is at 5000 Angstroms. The spectrum of a star that is
twice as hot, with
a temperature of 11,600K, peaks at:
a) 2500 Angstroms.
b) 10,000 Angstroms.
c) 20,000 Angstroms.
d) 1250 Angstroms.
e) 5000 Angstroms.
59. Atom A has 8 protons,
8 electrons, and
8 neutrons.
Atom B has 8 protons,
7 electrons, and
8 neutrons.
Therefore:
a) Atom A has a mass
approximately 16/15 times
larger than Atom B.
b) Atom A and Atom B are both
lithium atoms.
c) Atom A and Atom B are isotopes
of each other.
d) Atom A is an ion.
e) Atom B is an ion.
60. An emission-line spectrum is produced by:
a) A hot solid object.
b) A hot very dense gas.
c) A low density gas cloud in front of a source of continuous
light.
d) A vapor lamp, like the ones shown in class.
e) A star like the Sun.
61. When an electron in
an atom spontaneously jumps from a higher
energy level to a lower energy level,
the atom:
a) emits a photon of light.
b) absorbs a photon of light.
c) becomes excited.
d) becomes ionized.
e) becomes an isotope.
62. Bob weighs 150 lbs and Pete weights 300 lbs.
The distance of Bob from their center of mass is:
a) the same as the distance of Pete from their center of mass.
b) half the distance of Pete from their center of mass.
c) twice the distance of Pete from their center of mass.
d) four times the distance of Pete from their center of mass.
e) one-quarter the distance of Pete from their center of mass.
63.
If a laser is moving at high speeds towards an observer,
the light the observer sees has:
a) a higher frequency than if the laser were at rest with
respect to the observer.
b) a low frequency than if the laser were at rest with
respect to the observer.
c) a longer wavelength than if the laser were at rest with
respect to the observer.
d) the same wavelength as if the laser were at rest with
respect to the observer.
e) a lower speed than if the laser were at rest with
respect to the observer.
64. An atom of deuterium has a mass approximately equal to
that of:
a) an atom of ordinary hydrogen.
b) two atoms of ordinary hydrogen.
c) a 4He atom.
d) a 12C atom.
e) a 14C atom.
65. The luminosity of a star is:
a) its brightness.
b) the total energy it emits in its lifetime.
c) the rate at which it emits energy in all directions.
d) the color of the star.
e) the peak of the star's spectrum.
66. What property of an atom determines what
chemical element it is?
a) its mass.
b) the number of electrons.
c) the number of protons.
d) the number of neutrons.
e) the total number of protons plus neutrons.
67. Which of the following types
of light has the
highest frequency?
a) Gamma rays.
b) Visible light.
c) Radio waves.
d) Infrared light.
e) Ultraviolet light.
68. Microwaves:
a) have shorter wavelengths than ultraviolet light.
b) have wavelengths between those of UV and visible light.
c) have shorter wavelengths than gamma rays.
d) have wavelengths between those of X-rays and gamma rays.
e) have wavelengths between infrared and radio waves (or are short wavelength radio waves).
69. Which of the following properties of an astronaut
remains constant, whether they are on the Earth, on the Moon, or
in orbit
around the Earth?
a) acceleration.
b) weight.
c) mass.
d) the
gravitational field they are in.
e) velocity.
70. According to Kirchoff's Laws, what produces an absorption-line
spectrum?
a) a low density gas.
b) a hot solid.
c) a hot dense gas.
d) a hot solid or hot dense gas behind a low density gas.
e) a vapor lamp.
71. Star A has a mass of M1, and Star B
has a
mass of M2. Star A's distance from the center
of mass of the pair is X1, while
Star B's distance
from the center of mass is X2.
The equation that relates these four quantities is:
a) X1X2 = M1M2.
b) M1X12 =
M2X22.
c) M1X1 = M2X2.
d) M1/X1 = M2/X2.
e) M1X13
= M2X23.
72. Star A and Star B are in a binary pair.
Star A has a mass three times that of Star B.
Star A's distance from the center
of mass of the pair is 100 light years. How far is Star B from
the center of mass?
a) 100 light years.
b) 100/3 = 33.3 light years.
c) 100 X 3 = 300 light years.
d) 100 X 32 = 900 light years.
e) 100/32 = 11.1 light years.
73. As a planet orbits around a star in an elliptical orbit,
which of the following remains a constant?
a) the velocity.
b) the speed.
c) the kinetic energy.
d) the potential energy.
e) the kinetic plus potential energy.
74. The peak of the thermal spectrum of a planet
is typically in the:
a) visible.
b) X-ray.
c) ultraviolet.
d) infrared.
e) gamma ray.
75.
The frequency of light is:
a) measured in Joules.
b) measured in Watts.
c) measured in Angstroms.
d) measured in Hertz.
e) measured in meters.
76. 273 degrees Kelvin is:
a) 0 deg Celsius.
b) The freezing point of water.
c) 32 deg Fahrenheit.
d) 273K above absolute zero.
e) all of the above.
77. What produces a
thermal (blackbody) continuous spectrum?
a) a low density gas.
b) a high density gas or solid.
c) a low density gas in front of a high density gas.
d) a low density gas in front of a solid.
e) all of the above.
78. Which of the following systems produces an absorption-line
spectrum?
a) A star like the Sun.
b) A burner on a stove.
c) The filament in an ordinary light bulb.
d) The vapor lamps shown in class, with low density gases inside.
e) An isolated interstellar cloud of gas, with no bright sources behind.
79. The boiling point of water is:
a) 273K.
b) 373K.
c) 32K.
d) 212K.
e) 0K.
80. Which of the following types
of light has a frequency between that of X-rays and that of visible light?
a) Gamma rays.
b) Microwaves.
c) Radio waves.
d) Infrared light.
e) Ultraviolet light.
81. The unit 1/second (or wavelength/sec or cycle/sec) is called
a/an:
a) Joule.
b) Watt.
c) Hertz.
d) Angstrom.
e) Kelvin.
82. Deuterium is:
a) Helium with two protons and no neutrons.
b) Helium with two protons and two neutrons.
c) Hydrogen with one proton and no neutrons.
d) Hydrogen with one proton and one neutron.
e) Hydrogen with one proton and two neutrons.
83. Star A has a photospheric temperature two times larger than that
of Star B. Therefore,
the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star A is:
a) two times larger than that of Star B.
b) 1/2 that of Star B.
c) four times larger than that of Star B.
d) 1/4 that of Star B.
e) the same as that of Star B.
84. Atom A has 6 protons,
6 electrons, and
7 neutrons.
Atom B has 6 protons,
5 electrons, and
7 neutrons.
Therefore:
a) Atom A and Atom B are isotopes of each other.
b) Atom A and Atom B are both ions.
c) Atom A is an ion, but not Atom B.
d) Atom B is an ion, but not Atom A.
e) Atom A has a mass that is approximately
(6+6)/(6+5) = 12/11 times that of Atom B.
85. The three rules that describe when a particular
type of spectrum (i.e., continuous, emission line,
or absorption line) is produced are called:
a) Kepler's Laws.
b) Angstrom's Laws.
c) Wien's Laws.
d) Stefan's Laws.
e) Kirchoff's Laws.
86. A low density gas in front of a high density gas produces a/an:
a) emission-line spectrum.
b) absorption-line spectrum.
c) continuous spectrum.
d) blackbody spectrum.
e) bright-line spectrum.
87. An astronaut in the Space Station in orbit around the Earth:
a) has a constant velocity.
b) is accelerating towards the Earth.
c) has a mass of zero.
d) is not affected by gravitational forces.
e) has the same weight, if he/she steps onto a bathroom scale,
as if he/she was on Earth.
88. 373K is equal to:
a) 212 deg F.
b) 32 deg F.
c) 100 deg F.
d) 0 deg F.
e) 273 deg F.
89. A Hertz is a unit of:
a) Power.
b) Energy.
c) Frequency.
d) Wavelength.
e) Time.
90. Kirchoff's Laws describe:
a) How planets orbit around the Sun.
b) How the luminosity of a star relates to its temperature.
c) How the luminosity and the brightness of a star relate to its distance.
d) How the temperature of a star corresponds to the peak of its spectrum.
e) When a particular type of spectrum is produced.
91. A hot star like Vega, almost twice as hot as the Sun in
the Kelvin temperature scale, has a spectrum which peaks in the:
a) visible.
b) radio.
c) ultraviolet.
d) infrared.
e) gamma ray.
92. In the energy level diagram of hydrogen, the levels
get closer and closer together as the energy increases.
The red H-alpha emission line of hydrogen
is produced when an electron jumps from energy level
3 to energy level 2 in a hydrogen atom, while a jump
from level 4 to level 2 produces the
blue-green H-beta line and a jump from level 2 to level 1 produces
UV light.
A jump from level 4 to level 3 produces:
a) infrared light.
b) gamma rays.
c) X-rays.
d) radio waves.
e) orange light.
93. Pete has a mass four times that of Jane.
If Pete is 1 meter from their center of mass, how far from
the center of mass is Jane?
a) 1 meter.
b) 4 meters.
c) 42 = 16 meters.
d) 1/4 meters.
e) 1/42 = 1/16 meters.
94. An atom with 6 protons, 8 neutrons, and 5 electrons is:
a) an ion of carbon.
b) an isotope of an atom with 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 5 electrons.
c) about 14/12 times more massive than an atom with 6 protons,
6 neutrons, and 5 electrons.
d) positively charged.
e) all of the above.
95. The process of an atom losing an electron is called:
a) excitation.
b) de-excitation.
c) Doppler shifting.
d) ionization.
e) making an isotope.
96. What is the mathematical relationship between
luminosity L and brightness b?
(note: brightness is sometimes called "flux").
a) L = b.
b) L = b/(4*pi*D), where D is the distance.
c) L = b/(4*pi*D2), where D is the distance.
d) b = L/(4*pi*D), where D is the distance.
e) b = L/(4*pi*D2), where D is the distance.
97. The equation that relates the wavelength of
the peak of the thermal spectrum
lambda(max)
of an object to the temperature T of this object is called:
a) Wien's Law.
b) Stefan's Law.
c) Doppler's Law.
d) The Stefan-Boltzmann Law.
e) Kirchoff's Law.
98. The quantity 89.5 MHz equals:
a) 89.5 km/s.
b) 89.5 Joules/sec.
c) 89.5 X 106 1/sec.
d) 89.5 meters.
e) 89.5 Calories/sec.
99. A blackbody spectrum is:
a) an emission-line spectrum.
b) a continuous spectrum.
c) an absorption-line spectrum.
d) produced by a low density gas.
e) a bright-line spectrum, where only certain colors of the rainbow
are seen.
100. Star A has a surface temperature half that of Star B.
Therefore, the wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of Star A is:
a) twice that of Star B.
b) four times that of Star B.
c) one half that of Star B.
d) one quarter that of Star B.
e) one 16th that of Star B.
101. The highest energy photons are:
a) Ultraviolet.
b) X-rays.
c) Visible light.
d) Radio waves.
e) Gamma rays.
102.
Wien's Law relates:
a) The frequency of light to its wavelength.
b) The luminosity of a solid or dense gas to its temperature.
c) The amount spectral lines are shifted and velocity of the
source of light.
d) The orbital period of a planet around the Sun and the semi-major
axis of its orbit.
e) The temperature of a solid or dense gas (in the Kelvin scale) and the wavelength
of the peak of its spectrum (lambda(max)).
103. A cat and a dog sit on two ends of a board that is balanced on a rock.
The dog weighs three times as much as the cat. If the board is perfectly
balanced on the rock, so that it is horizontal (parallel to
the ground), how far is the dog from the rock?
a) Three times further from the rock than the cat is.
b) Nine as far from the rock as the cat is.
c) One third the distance from the rock that the cat is.
d) One ninth the distance from the rock that the cat is.
e) The same distance from the rock as the cat.
104. Atom A has 6 protons,
6 electrons, and
6 neutrons.
Atom B has 6 protons,
5 electrons, and
6 neutrons.
Therefore:
a) Atom A and Atom B are different elements.
b) The mass of Atom A is 12/11 times that of Atom B.
c) Atom A and Atom B are isotopes
of each other.
d) Atom A is an ion.
e) Atom B is an ion.
105. Which of the following is true about the Moon?
a) It is in a stable orbit, so it is not accelerating.
b) It is orbiting the Earth at a constant velocity.
c) The gravitational force the Moon exerts on the Earth is considerably
less than the gravitational force the Earth exerts on the Moon.
d) Because the Moon is in space, it has no inertia.
e) It is accelerating towards the Earth.
106. Which of the following objects has a spectrum that peaks
in the ultraviolet?
a) The Sun.
b) A star much hotter than the Sun, for example, Vega.
c) A star much colder than the Sun, for example, Betelgeuse.
d) A human being.
e) A planet like the Earth.
107. Kirchoff's Third Law states:
a) the planets orbit the Sun in ellipses, not circles.
b) the temperature of a star is inversely correlated with
the wavelength of the peak of its spectrum.
c) an absorption-line spectrum is produced by low density gas
in front of a source of continuous light.
d) a solid or a dense gas produces a continuous spectrum.
e) the luminosity of a star is proportional to its temperature
raised to the 4th power.
108.
X-rays have wavelengths in between those of:
a) Ultraviolet light and Gamma rays.
b) Infrared and radio waves.
c) Visible light and radio waves.
d) Microwaves and infrared light.
e) Visible light and ultraviolet light.
109. During a total solar eclipse, the
photosphere of the Sun is completely blocked by the Moon, however,
the low density atmosphere of the Sun is visible.
If one obtains
a spectrum of the solar atmosphere during a total solar eclipse,
what kind of spectrum is observed?
a) A continuous spectrum.
b) An absorption line spectrum.
c) An emission line spectrum.
d) A blackbody spectrum.
e) A dark-line spectrum.
110. The mass of a neutron is:
a) About the same as the mass of a proton.
b) About the same as the mass of an electron.
c) About 2000 times the mass of a proton.
d) About 1/2000th the mass of a proton.
e) About 1/2000th the mass of an electron.
111. Which kind(s) of light has/have wavelengths less than
that of visible light?
a) Only X-rays.
b) Ultraviolet, X-rays, and Gamma Rays.
c) X-rays, Gamma Rays, and Infrared.
d) Radio waves and Infrared.
e) Radio waves and Ultraviolet.
112.
Which of the following statements is correct?
a) X-ray photons have lower energy and lower frequency than Gamma rays.
b) X-ray photons have higher energy and lower frequency than Gamma rays.
c) X-ray photons have lower energy and higher frequency than Gamma rays.
d) X-ray photons have higher energy and higher frequency than Gamma rays.
e) X-ray photons have higher mass and lower energy than Gamma rays.
113.
The wavelength of the peak of the spectrum of a hot solid ball of metal due to
blackbody radiation is:
a) Proportional to its temperature.
b) Proportional to the square of its temperature.
c) Proportional to its temperature to the fourth power.
d) Inversely proportional to its temperature.
e) Inversely proportional to the square of its temperature.
114. A cat is chasing a squirrel.
The squirrel jumps on one end of a seesaw, the cat on the other.
The board balances horizontally when the squirrel is 4 feet from
the balance point, and the cat is 1 foot from the balance point.
If the cat weighs 8 pounds, how much does the squirrel weigh?
a) 1/2 pound.
b) 1 pound.
c) 2 pounds.
d) 4 pounds.
e) 8 pounds.
115. The mass of a proton is:
a) About the same as that of an electron.
b) About two thousand times that of a neutron.
c) About the same as that of a photon.
d) About 2000 times less than that of a neutron.
e) About the same as that of a neutron.
116. The Hubble Space Telescope is in orbit around the Earth.
Its acceleration is:
a) zero.
b) in the direction of its motion along its orbit.
c) downwards towards the Earth.
d) upwards away from the Earth.
e) in a direction opposite its direction of motion
in its orbit.
117. The luminosity of a star is proportional to
its temperature to the fourth power. This rule is called:
a) Stefan's Law.
b) Kepler's Law.
c) Angstrom's Law.
d) Wien's Law.
e) Kirchoff's Law.
118. A Watt is equal to:
a) 1 MHz.
b) 1 meter/second.
c) 1/sec.
d) 1 Joule/sec.
e) 1010 Angstrom.
119. If the Sun were 5 A.U. away from us, how would its brightness
change, relative to what it is now?
a) It would DECREASE by a factor of 5.
b) It would DECREASE by a factor of 52 = 25.
c) It would DECREASE by a factor of 54 = 625.
d) It would INCREASE by a factor of 5.
e) It would not change.
120. Which of the following scientists first showed that white light
is made up of all of the colors of the rainbow?
a) Einstein.
b) Galileo.
c) Stefan.
d) Wien.
e) Newton.
121. What do scientists call the process when an
electron in an atom gains energy and jumps to a higher energy level?
a) Isotopization.
b) Excitation.
c) Ionization.
d) De-excitation.
e) Doppler Shift.
122.
What kind of spectrum does the Sun have?
a) An emission-line spectrum.
b) A continuous spectrum.
c) An absorption-line spectrum.
d) A blackbody spectrum.
e) A thermal spectrum.
123. An atom that has lost an electron is:
a) Excited.
b) Ionized.
c) Isotopized.
d) Dopplerized.
e) De-Excited.
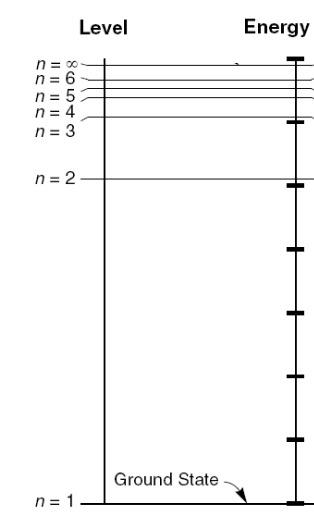 124. The energy level diagram of hydrogen is shown in the drawing
to the right.
The energy difference between level 3 and level 2 corresponds to
the energy of the red H-alpha photon.
The energy difference between level 4 and level 2 corresponds to
the energy of the blue-green H-beta photon.
The energy difference between level 4 and 3 corresponds to the
energy of a/an:
124. The energy level diagram of hydrogen is shown in the drawing
to the right.
The energy difference between level 3 and level 2 corresponds to
the energy of the red H-alpha photon.
The energy difference between level 4 and level 2 corresponds to
the energy of the blue-green H-beta photon.
The energy difference between level 4 and 3 corresponds to the
energy of a/an:
a) infrared photon.
b) gamma ray photon.
c) orange photon.
d) ultraviolet photon.
e) x-ray photon.
125.
100 degrees Celsius is:
a) 373 Kelvin.
b) 100 Kelvin.
c) 32 Kelvin.
d) 273 Kelvin.
e) 212 Kelvin.
126. If a star is moving away from us, the light we observe
from the star has longer wavelengths than if the star was at rest
relative to us. This phenomenon is called a:
a) Parallax Shift.
b) Precession Shift.
c) Retrograde Shift.
d) Excitation.
e) Doppler Shift.
127. The vapor lamps shown in class produce light at only
certain specific wavelengths. This light is produced by:
a) electrons in lower energy levels of
atoms
jumping to higher energy levels.
b) a hot dense solid in the lamp.
c) a low density gas in front of a hot dense solid.
d) electrons in high energy levels of the atoms in the gas
jumping to lower energy levels.
e) electrons escaping from atoms.
128. Planet A and Planet B have the same mass, but Planet
A has a diameter two times larger. Therefore:
a) The escape velocity from the surface of Planet A is larger
than that from the surface of Planet B.
b) The escape velocity from the surface of Planet A is smaller
than that from the surface of Planet B.
c) The escape velocity from the surfaces of the two planets
are the same.
d) The escape velocity also depends upon the mass of the object
trying to escape from the surface.
e) The escape velocity from the surface of a planet does not
depend upon the radius of the planet.
129. Which of the following types of light has the fastest
speed in a vacuum?
a) Radio waves.
b) Gamma rays.
c) X-rays.
d) Ultraviolet light.
e) They all have the same speed in a vacuum.
 130. The energy level diagram of hydrogen is shown in the drawing
to the right.
The energy difference between level 3 and level 2 corresponds to
the energy of the red H-alpha photon.
The energy difference between level 4 and level 2 corresponds to
the energy of the blue-green H-beta photon.
The energy difference between level 2 and 1 corresponds to the
energy of a/an:
130. The energy level diagram of hydrogen is shown in the drawing
to the right.
The energy difference between level 3 and level 2 corresponds to
the energy of the red H-alpha photon.
The energy difference between level 4 and level 2 corresponds to
the energy of the blue-green H-beta photon.
The energy difference between level 2 and 1 corresponds to the
energy of a/an:
a) infrared photon.
b) radio photon.
c) orange photon.
d) ultraviolet photon.
e) microwave photon.
Answers: 1c, 2a, 3d, 4d, 5c, 6d, 7d, 8b, 9e,
10e, 11c, 12c, 13b, 14c, 15b, 16b,
17b, 18a, 19d, 20e, 21a, 22c, 23c, 24c, 25a, 26b,
27e, 28a, 29a, 30d, 31c, 32d, 33e, 34d, 35a, 36d, 37d,
38a, 39b, 40c, 41e, 42e, 43c, 44a, 45a, 46a, 47b,
48c, 49d, 50a, 51a, 52c, 53e, 54b, 55b, 56b, 57d, 58a,
59e, 60d, 61a, 62c, 63a, 64b, 65c, 66c, 67a,
68e, 69c, 70d, 71c, 72c, 73e, 74d, 75d, 76e, 77b, 78a,
79b, 80e, 81c, 82d, 83b, 84d, 85e, 86b, 87b, 88a, 89c, 90e,
91c, 92a, 93b, 94e, 95d, 96e, 97a, 98c, 99b, 100a,
101e,
102e, 103c,
104e, 105e, 106b, 107c, 108a, 109c, 110a,
111b, 112a,
113d, 114c,
115e, 116c,
117a, 118d,
119b, 120e,
121b, 122c,
123b, 124a,
125a, 126e, 127d,
128b, 129e,
130d.
 124. The energy level diagram of hydrogen is shown in the drawing
to the right.
The energy difference between level 3 and level 2 corresponds to
the energy of the red H-alpha photon.
The energy difference between level 4 and level 2 corresponds to
the energy of the blue-green H-beta photon.
The energy difference between level 4 and 3 corresponds to the
energy of a/an:
124. The energy level diagram of hydrogen is shown in the drawing
to the right.
The energy difference between level 3 and level 2 corresponds to
the energy of the red H-alpha photon.
The energy difference between level 4 and level 2 corresponds to
the energy of the blue-green H-beta photon.
The energy difference between level 4 and 3 corresponds to the
energy of a/an: