ASTR 1020 SPRING 2020: QUIZ #3
VERSION B
Write your name at the top of this quiz as well as on
your answer sheet. WRITE YOUR VERSION ON YOUR ANSWER SHEET.
Feel free to write or draw on the quiz.
PICK THE BEST ANSWER FOR EACH PROBLEM.
1. If a star cluster contains
M, K, G, F, and A stars, but no B or O stars, how
old is it?
a) 1 million years old.
b) 1 billion years old.
c) 10 billion years old.
d) 100 billion years old.
e) 1 trillion years old.
b) 1 billion years old.
2. The diffuse reddish light arising from HII regions
in the visible is mainly from:
a) the spin-flip transition of hydrogen atoms.
b) emission lines from hydrogen and other atoms.
c) blackbody emission from interstellar dust grains.
d) emission lines from molecular hydrogen.
e) emission lines from carbon monoxide molecules.
b) emission lines from hydrogen and other atoms.
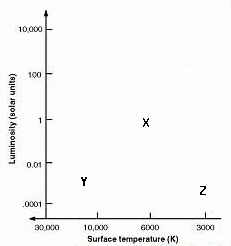 3. The locations of Stars X, Y,
and Z are marked on the H-R diagram to the right.
What types of stars are they?
3. The locations of Stars X, Y,
and Z are marked on the H-R diagram to the right.
What types of stars are they?
a) Star X: main sequence B star.
Star Y: white dwarf star.
Star Z: main sequence A star.
b) Star X: GV star.
Star Y: main sequence A star.
Star Z: supergiant M star.
c) Star X: giant G star.
Star Y: AV star.
Star Z: MV star.
d) Star X: GIII star.
Star Y: white dwarf star.
Star Z: main sequence M star.
e) Star X: G star with hydrogen fusion in core.
Star Y: white dwarf star.
Star Z: main sequence M star.
e) Star X: G star with hydrogen fusion in core.
Star Y: white dwarf star.
Star Z: main sequence M star.
4. Which of the following types of stars are the most
massive?
a) B2V.
b) M2V.
c) G2V.
d) K2V.
e) A2V.
a) B2V.
5.
A mass of 1.4 solar masses is:
a) The upper mass limit for a neutron star.
b) The upper mass limit for a brown dwarf.
c) The upper mass limit for a white dwarf.
d) The mass of a M2V star.
e) The mass of a O9V star.
c) The upper mass limit for a white dwarf.
6. The most massive stars in the Pleiades
are:
a) G stars.
b) M stars.
c) B stars.
d) F stars.
e) O stars.
c) B stars.
7. In Astronomy, a plot of brightness vs.
time is called a:
a) wave curve.
b) proper motion curve.
c) blackbody plot.
d) Hertzsprung-Russell diagram.
e) light curve.
e) light curve.
8. Interstellar dust:
a) emits mostly thermal radiation
in the UV and optical light.
b) Emits mostly thermal radiation
in the gamma ray.
c) contributes about half of the mass
of the interstellar medium.
d) Makes background stars appear redder
than they really are.
e) Is hypothesized to exist, but
has never been detected.
d) Makes background stars appear redder
than they really are.
9. Which of the following objects has
a spectrum that peaks in the long wavelength infrared?
a) an interstellar dust grain.
b) a main sequence B star.
c) a main sequence O star.
d) a white dwarf.
e) the Sun.
a) an interstellar dust grain.
10. What is one way to determine the radius of a star?
a) measure its proper motion.
b) If it is part of a visual binary pair, measure the
period of its orbit.
c) If it is part of an eclipsing binary star, time the eclipse.
d) All of the above.
e) None of the above methods work for any stars.
c) If it is part of an eclipsing binary star, time the eclipse.
11.
The plutonium on Earth was probably produced:
a) in the core of the Sun.
b) in the core of a red giant.
c) in a white dwarf.
d) in a planetary nebula.
e) in a supernova explosion.
e) in a supernova explosion.
12. Which kind of star sometimes
pulsates wildly in radius on a timescale
of approximately a year, causing large variations
in the brightness of the star with time?
a) isolated G2V stars.
b) isolated white dwarf stars.
c) isolated asymptotic giant branch stars.
d) stars like the Sun.
e) all of the above.
c) isolated asymptotic giant branch stars.
13. What is an AGB star?
a) a white dwarf star.
b) a main sequence star with a mass greater than 6-8 solar masses.
c) a protostar.
d) an evolved star nearing the end of its life.
e) a brown dwarf.
d) an evolved star nearing the end of its life.
14. Interstellar clouds are:
a) 1 percent hydrogen by mass.
b) 10 percent hydrogen by mass.
c) 50 percent hydrogen by mass.
d) 75 percent hydrogen by mass.
e) 99 percent hydrogen by mass.
d) 75 percent hydrogen by mass.
15. Which of the following objects has
the smallest radius?
a) a white dwarf.
b) a G2V star.
c) a M2V star.
d) a M2I star.
e) a O9V star.
a) a white dwarf.
16. Looking at the periodic table
on the wall, determine what is produced
when an alpha capture process happens to
24Mg?
a) 28Si
b) 28Al
c) 26Mg
d) 26Si
e) 28S
a) 28Si
 17. In the diagram shown to the right, what is the total
expected lifetime of star Z?
17. In the diagram shown to the right, what is the total
expected lifetime of star Z?
a) less than 1 million years.
b) 1 billion years.
c) 10 billion years.
d) 100 billion years.
e) 1 trillion or more years.
e) 1 trillion or more years.
 18. In the diagram shown to the right, what is the
evolutionary relationships between stars X,Y, and Z?
18. In the diagram shown to the right, what is the
evolutionary relationships between stars X,Y, and Z?
a) Star Z will evolve into a star like X.
b) Star Y will evolve into a star like X.
c) Star X will evolve into a star like Y.
d) Star X will evolve into a star like Z.
e) Star Y will evolve into a star like Z.
c) Star X will evolve into a star like Y.
19. Immediately after a one solar mass star leaves the main
sequence, and starts moving through the subgiant (IV) portion
of the H-R diagram, what is occuring inside the star?
a) helium fusion in the core, hydrogen fusion in a shell
surrounding the core.
b) hydrogen fusion in the core, helium fusion in a shell
surrounding the core.
c) no fusion in the core, hydrogen fusion in a shell
surrounding the core.
d) no fusion in the core, helium fusion in a shell
surrounding the core.
e) carbon fusion in the core, helium fusion in a shell
surrounding the core.
c) no fusion in the core, hydrogen fusion in a shell
surrounding the core.
20. To detect the strong spin-flip line from atomic hydrogen,
what kind of telescope is used?
a) an X-ray telescope.
b) a visible-light telescope.
c) a radio telescope.
d) a gamma ray telescope.
e) an ultraviolet telescope.
c) a radio telescope.
 3. The locations of Stars X, Y,
and Z are marked on the H-R diagram to the right.
What types of stars are they?
3. The locations of Stars X, Y,
and Z are marked on the H-R diagram to the right.
What types of stars are they?