


Next: Chapter 23
Up: Chapter 22
Previous: Review
- #03
- The gravitational acceleration and escape speed equations are
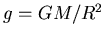 and
and
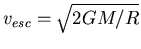 , for
, for 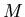 the object mass and
the object mass and 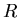 its spherical
radius. Here we have a
its spherical
radius. Here we have a 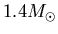 neutron star with a radius of
10 km, or
neutron star with a radius of
10 km, or 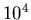 m. Converting to kg, the mass is
m. Converting to kg, the mass is
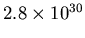 kg.
The gravitation acceleration is then
kg.
The gravitation acceleration is then
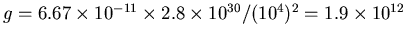 m/s
m/s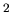 . The escape
speed is
. The escape
speed is
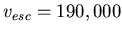 km/s (notice that I did the unit conversion
from m to km). If the radius were 4 km, the escape speed goes up by
the factor of
km/s (notice that I did the unit conversion
from m to km). If the radius were 4 km, the escape speed goes up by
the factor of
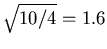 , giving a value of just about the speed
of light itself. This suggests that 4 km is the smallest size for a neutron
star of this mass.
, giving a value of just about the speed
of light itself. This suggests that 4 km is the smallest size for a neutron
star of this mass.
- #07
- Speed is distance over time. In this case we need the circumference divided
by the rotation period. At 1000 times/sec, the period must be 0.001 sec.
The circumference is
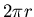 , and we are told
, and we are told 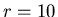 km, so the
circumference is about 60,000 m. Dividing these two gives
60 million m/s, or 60,000 km/s, which is about 20% of the speed of
light (or
km, so the
circumference is about 60,000 m. Dividing these two gives
60 million m/s, or 60,000 km/s, which is about 20% of the speed of
light (or 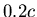 ). The circular orbit speed is
). The circular orbit speed is
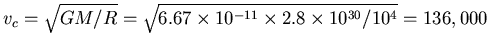 km/s,
which is about
km/s,
which is about 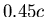 .
.



Next: Chapter 23
Up: Chapter 22
Previous: Review
Rico Ignace
2004-09-10