


Longitude (L) - angular coordinate measure around the Earth (East and West)
Latitude (B) - angular coordinate measure between the poles on the Earth (North and South)
Prime Meridian - zero degrees longitude; the prime meridian passes through Greenwich, England
Equator (Eq) - zero degrees latitude
North and South Poles - where media meet along the Earth's axis of rotation
Great Circles - a circle centered on the Earth
Horizon - the "sky line", i.e. the line that traces where the sky apparently meets the land
Azimuth (Az) - angular coordinate measure around the horizon, starting from the North point and moving Eastward
Altitude (Alt) - angular measure above the horizon along a great circle passing through the zenith
North Point - the point that is on the horizon and directly North
Zenith - the point directly above
Nadir - the point directly below
Meridian - the great circle that passes from the North point through the zenith to the South point
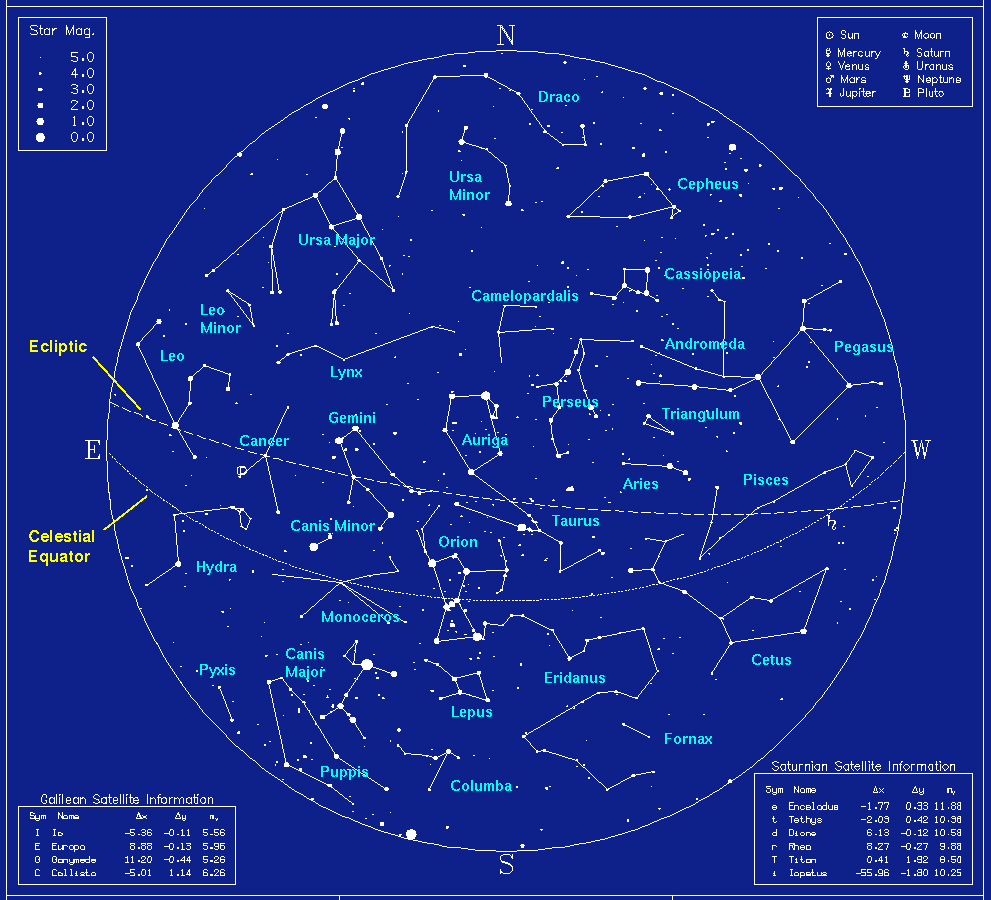
Right Ascension (RA) - similar to Earth longitude but for the sky; RA is measured Eastward starting from the Vernal Equinox
Declination (Dec) - similar to Earth latitude but for the sky; Dec is positive in the North Celestial Sphere and negative in the South
North Celestial Pole (NCP) - projection of North Pole onto the sky
South Celestial Pole (SCP) - projection of South Pole onto the sky
Celestial Equator (CE) - projection of equator onto the sky
Ecliptic - apparent path of the Sun over the course of one year
Vernal Equinox - first day of spring; the Sun lies exactly over the equator and is passing into the N. hemisphere
Autumnal Equinox - first day of autumn; the Sun lies exactly over the equator and is passing into the S. hemisphere
Summer Solstice - first day of summer; the Sun is highest in the sky for N. observers (lowest for S. observers)
Winter Solstice - first day of winter; the Sun is lowest in the sky for N. observers (highest for S. observers)