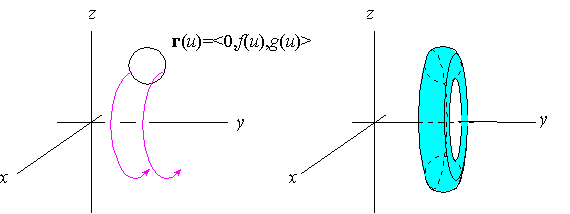Exercises
Use a graphing calculator or computer algebra system to
sketch each surface and then find the level surface representations of each
of the following parametric equations.
|
|
| |
r =
á vsin( u) ,vcos( u),v
ñ |
| | | |
r =
á vsin( u),v,vcos( u)
ñ |
|
| |
r =
á sin( u) cos( v),cos( u) ,sin( u) sin( v)
ñ |
| | | |
r =
á sin( v) sin( u) ,cos( v) sin( u) ,cos(u)
ñ |
|
| |
r =
á 2sin( u) cos( v),3cos( u) ,2sin( u) sin( v)
ñ |
| | | |
r =
á 2sin( u)cos( v) ,2cos( u) ,sin( u) sin( v)
ñ |
|
| |
r =
á sin( u) cosh( v),sinh( v) ,cos( u) cosh( v)
ñ |
| | | |
r =
á sin( u)cosh( v) ,sin( u) sinh( v) ,cos( u)
ñ |
|
| |
r =
á sec( u) sin( v),sec( u) cos( v) ,tan( u)
ñ |
| | | |
r =
á vsin( u),vcos( u) ,v2sin( 2u)
ñ |
|
| |
r =
á evsin( u) ,evcos(u) ,e-v
ñ |
| | | |
r =
á sin( v) cos( u) ,sin( v) sin(u) ,sin2( v) cos( 2u)
ñ |
|
|
|
|
Find ru and rv for each of the following surfaces. Compute their dot product to determine
if the parametrization is orthogonal or not.
|
|
| |
r =
á vsin( u) ,vcos( u),uv
ñ |
| | | |
r =
á vsin( u),v2,vcos( u)
ñ |
|
| |
r =
á sin( u) cos( v),cos( u) ,sin( u) sin( v)
ñ |
| | | |
r =
á sin( v)sin( u) ,cos( v) sin( u) ,cos(u)
ñ |
|
| |
r =
á evsin( u) ,evcos(u) ,e-v
ñ |
| | | |
r =
á 2sin( u) cos( v) ,2cos( u) ,sin(u) sin( v)
ñ |
|
|
|
|
Find the equation of the tangent plane to r(u,v) at the point r( p,q) for
the given ( p,q) .
|
|
| |
r =
á vsin( u) ,vcos( u),uv
ñ |
| | | |
r =
á vsin( u),v2,vcos( u)
ñ |
|
| | | | |
| |
r =
á vsin( u) ,vcos( u),v
ñ |
| | | |
r =
á sin( v)sin( u) ,cos( v) sin( u) ,cos(u)
ñ |
|
| | | | |
| |
r =
á evsin( u) ,evcos(u) ,e-v
ñ |
| | | |
r =
á sin( u) cosh( v) ,sin( u) sinh(v) ,cos( u)
ñ |
|
| | | | |
|
|
|
Find the surface of revolution obtained by revolving the
following surfaces about the x-axis. Then find ru and rv and determine if the parametrization is
orthogonal.
|
|
| | | | |
| | | | |
| |
y = cosh( x) , x in [ -1,1] |
| | | |
y = sin( x) , x in [ 0,p] |
|
|
|
|
31. The helicoid is the surface parametrized by
|
r( u,v) =
á sinh( v) cos(u) ,sinh( v) sin( u) ,u
ñ |
|
Graph the helicoid for (u,v) in [0,2p]×[0,1]. How is the helicoid related to a helix? Is the
parametrization orthogonal?
32. A catenoid is the surface parametrized by
|
r( u,v) =
á cosh( v) cos(u) ,cosh( v) sin( u) ,v
ñ |
|
Graph both the catenoid and the helicoid in exercise 31. How are they
similar? How do they differ?
33. A Mobius strip is a surface parametrized by
|
r( u,v) = |  |
cos( u) +vcos |
æ
è
|
|
u
2
|
ö
ø
|
cos( u) ,sin( u) +vcos |
æ
è
|
|
u
2
|
ö
ø
|
sin( u) ,vsin |
æ
è
|
|
u
2
|
ö
ø
|  |
|
|
for u in [ 0,2p] and v in [ -0.3,0.3] .
Graph the Mobius strip with either a graphing calculator or a computer. What
is the parametrization of its tangent plane when u = p and v = 0.1? (see
problem 31)
34. Show that every parametric equation of the form
|
r( u,v) =
á f( v) cos(u) ,f( v) sin( u) ,f( v)
ñ |
|
is a parametrization of a section the cone x2+y2 = z2. Is the
parametrization orthogonal?
35. Use an identity for the hyperbolic trigonometric functions to
prove that
Then show that the Mercator parametrization
|
r( q,m) =
á R sech( m) cos( q) ,R sech( m) sin( q) ,Rtanh( m)
ñ |
|
is indeed a parametrization of the sphere of radius R centered at the
origin.
36. Show that r( t,u,v) =
á sin( t) cos( v) ,cos( t) cos(v) ,sin( u) sin( v) ,cos( u)sin( v)
ñ is a parametrization of the sphere in 4
dimensions given by
37. Find another parametrization of the sphere of radius R
centered at the origin by revolving the upper half circle
about the x-axis. Is the parametrization orthogonal?
38. If a curve r( v) =
á 0,f(u) ,g( u)
ñ for u in [ a,b]
is revolved about the y-axis, then the resulting surface of
revolution is parametrized by
|
r( u,v) =
á g( u) sin(v) ,f( u) ,g( u) cos( v)
ñ |
|
where ( u,v) is in[ a,b] ×[ 0,2p] .
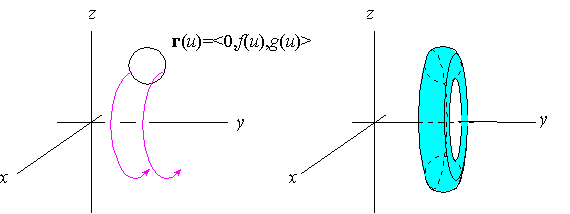
Find the parametrization of the torus which results from revolving the
circle
|
r( u) =
á 0,rcos( u) ,R+rsin( u)
ñ |
|
for u in [ 0,2p] about the y-axis, where R > r > 0 are
constants.
39. Determine the longitude q0 and
latitude j0 of your present location, and then use (2) to find rq, rj, and
the equation of the tangent plane to the earth at your location.
40. Write to Learn: Find the formula for revolving y = f(x) , x in [ a,b] , about the
z-axis. Present and
explain your formula in a short essay.
41. Write to Learn: Stereographic projection assigns to each point (u,v,0) the point ( x,y,z) on the unit sphere that is
on the line from the point (0,0,1) through the point (u,v,0) .
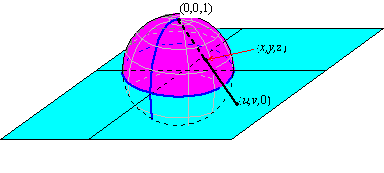
Use similar right triangles to show that stereographic projection leads to the
following parameterization of the sphere.
|
r( u,v) = |
|
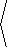
|
2u
u2+v2+1
|
, |
2v
u2+v2+1
|
, |
u2+v2-1
u2+v2+1
| 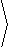 |
|
|