Exercises:
Find the image in the xy-plane of the given curve
in the uv-plane under the given transformation. If the
transformation is linear, identify it as such and write it in matrix form.
|
|
| |
T( u,v) =
á u,v2
ñ , v = 2u |
| | | |
T( u,v) =
á uv,u+v
ñ , v = 3 |
|
| |
T( u,v) =
á u-2v,2u+v
ñ , v = 0 |
| | | |
T( u,v) =
á u+3,v+2
ñ , u2+v2 = 1 |
|
| |
T( u,v) =
á 4u,3v
ñ , u2+v2 = 1 |
| | | |
T( u,v) =
á u2+v,u2-v
ñ , v = u |
|
| |
T( u,v) =
á u2-v2, uv
ñ , v = 2 |
| | | |
T( u,v) =
á u2-v2,2uv
ñ , u = -1 |
|
| |
T( r,q) =
á rcos( q),rsin( q)
ñ , r = 1 |
| | | |
T(r,q) =
á rcos( q) ,rsin(q)
ñ , q = p/4 |
|
|
|
|
Find the coordinate curves of the given transformation. Then
find the image of the unit square in the uv-plane under the given
transformation. If the transformation is linear, identify it as such and
write it in matrix form.
|
|
| | | | |
| | | | |
| |
T( u,v) =
á u2-v2, u + v
ñ |
| | | |
| |
T( u,v) =
á 2u+3v,-3u+2v
ñ |
| | | |
T( u,v) =
á ucos( pv) ,usin(pv)
ñ |
|
| |
Rotation about the origin |
| | | |
Rotation about the origin |
|
| | | | |
| | | | |
T( u,v) =
á u + v, u + v
ñ |
|
| |
T( r,q) =
á rcos( q),r2sin2( q)
ñ |
| | | |
T(r,t) =
á rcosh( t) ,rsinh( t)
ñ |
|
|
|
|
Find a conic in standard form that is the pullback under
rotation of the given curve. (You found the principal axes for these conics
in section 2-9).
31. For the conic 52x2-72xy+73y2 = 100, show that tan(q) = 3/4. Then explain why
|
cos( -q) = |
4
5
|
and sin( -q) = |
-3
5
|
|
|
and find the pullback under rotation through angle q of the given conic.
32. Find tan( q) for 73x2+72xy+52y2 = 100 and use it to determine cos(q) and sin(q) (see #31). Then find the pullback under rotation through angle q of the given conic.
33. Show that if
|
|
é
ê
ë
|
|
|
ù
ú
û
|
= |
é
ê
ë
|
|
|
ù
ú
û
|
|
é
ê
ë
|
|
|
ù
ú
û
|
|
|
then we must also have
|
|
é
ê
ë
|
|
|
ù
ú
û
|
= |
é
ê
ë
|
|
|
ù
ú
û
|
|
é
ê
ë
|
|
|
ù
ú
û
|
|
|
What is the significance of this result?
34. Use matrix multiplication to show that a rotation through an angle q followed by a rotation through an angle f is
equivalent to a single rotation through the angle q+f.
35. The parabolic coordinate system on the xy-plane is the
image of the coordinate transformation
Find the image of the horizontal lines u = 0,1,2 and the vertical lines v = 0,1,2 in the
parabolic coordinate system.
36. The tangent coordinate system on the xy-plane is the
image of the coordinate transformation
|
T( u,v) = |
|
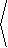
|
u
u2+v2
|
, |
v
u2+v2
| 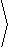 |
|
|
Find the image of the horizontal lines u = 0,1,2 and the vertical lines v = 0,1,2 in the
tangent coordinate system.
37. The elliptic coordinate system on the xy-plane is the
image of the coordinate transformation
|
T( u,v) =
á cosh( u) cos( v), sinh( u) sin( v)
ñ |
|
Find the image of the horizontal lines u = 0,1,2 and the vertical lines v = 0,1,2 in the elliptic coordinate system.
38. The bipolar coordinate system on the xy-plane is the
image of the coordinate transformation
|
T( u,v) = |
|
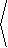
|
sinh( v)
cosh(v) -cos( u)
|
, |
sin( u)
cosh(v) -cos( u)
| 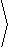 |
|
|
Find the image of the horizontal lines u = 0,1,2 and the vertical lines v = 0,1,2 in the
bipolar coordinate system.
39. Write to Learn: A coordinate transformation T( u,v) =
á f( u,v), g( u,v)
ñ is said
to be area preserving if the area of the image of any region S in
the uv-plane is the same as the area of R. Write a short essay
explaining why a rotation through an angle q is area preserving.
40. Write to Learn: What type of coordinate system is implied by the
coordinate transformation T( u,v) =
á u, F(u) + v
ñ? What are the coordinate curves? What is significant
about tangent lines to these curves? Write a short essay which addresses
these questions.
41.
Simplify (4) into (5)
using the double angle formula for the tangent function.