Part 1: Definition of the Integral
Iterated integrals are used primarily as a tool for computing double
integrals, where a double integral is an integral of f( x,y)
over a region R. In this section, we define double integrals and begin
examining how they are used in applications.
To begin with, a set of numbers { x0,xj,rj} , j = 1,¼,m, is said to be a tagged partition of [a,b] if
|
a = x0 < x1 < x2 < ¼ < xm = b |
|
and if xj-1 £ rj £ xj for all j = 1,...,m. Moreover, if we let Dxj = xj-xj-1, then the partition is said to be h-fine if Dxj £ h for all j = 1,¼,n.
If { x0,xj,rj} , j = 1,¼,m, is an h-fine
tagged partition of [ a,b] , and if {y0,yk,tk} , k = 1,¼,n is a l-fine tagged partition
of [ c,d] , then the rectangles [ xj-1,xj]×[ yk-1,yk] partition the rectangle [a,b] ×[ c,d] and the points (rj,tk) are inside the rectangles [ xj-1,xj]×[ yk-1,yk] .
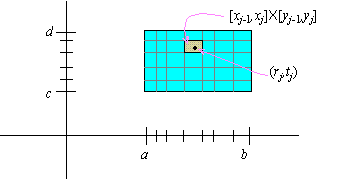
The Riemann sum of a function f( x,y) over this
partition of [ a,b] ×[ c,d] is
|
|
m
å
j = 1
|
|
n
å
k = 1
|
f( rj,tk) DxjDyk |
|
We then define the double integral of f( x,y) over [ a,b] ×[ c,d] to be the limit as h,l
approach 0 of Riemann sums over h,l fine partitions:
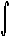  |
| [ a,b] ×[ c,d] |
|
f( x,y)dA = |
lim
h® 0
|
|
lim
l®0
|
|
m
å
j = 1
|
|
n
å
k = 1
|
f( sj,tk) DxjDyk |
|
To define the double integral over a bounded region R other than a
rectangle, we choose a rectangle [ a,b] ×[ c,d] that contains R,
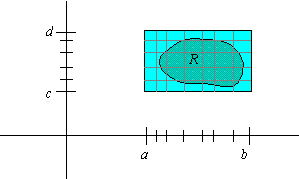
and we define g so that g( x,y) = f( x,y) if ( x,y) is in R and g( x,y) = 0 otherwise. The
double integral of f( x,y) over an arbitrary region R is
then defined to be
|
|
f( x,y) dA = |
|
g( x,y) dA |
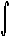 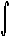 |
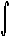 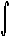 | |
R |
[ a,b] ×[c,d] |
|
It then follows from the definition that the double integral satisfies the
following properties:
  R
[ f( x,y) +g( x,y) ] dA R
[ f( x,y) +g( x,y) ] dA |
|
|
  R
f( x,y) dA + R
f( x,y) dA +   R
g( x,y) dA R
g( x,y) dA |
| (1) |
  R
[ f( x,y) -g( x,y) ] dA R
[ f( x,y) -g( x,y) ] dA |
|
|
  R
f( x,y) dA- R
f( x,y) dA-  R
g( x,y) dA R
g( x,y) dA |
| (2) |
  R
kf( x,y) dA R
kf( x,y) dA |
|
|
k  R
f( x,y) dA R
f( x,y) dA |
| (3) |
|
where k is a constant.
EXAMPLE 1 Evaluate the integral of f+g over R if
  R
f( x,y) dA= 3 and R
f( x,y) dA= 3 and
  R
g( x,y) dA = 2 R
g( x,y) dA = 2 |
| (4) |
Solution: We use property (1) to write
  R
[ f( x,y) +g( x,y) ] dA = R
[ f( x,y) +g( x,y) ] dA =
  R
f( x,y) dA + R
f( x,y) dA +   R
g( x,y) dA = 3+2 = 5 R
g( x,y) dA = 3+2 = 5 |
|
Check your Reading: What is the integral of f-g over R
given (4)?

R f( x,y) dA= 3 and
R g( x,y) dA = 2
R [ f( x,y) +g( x,y) ] dA =
R f( x,y) dA +
R g( x,y) dA = 3+2 = 5