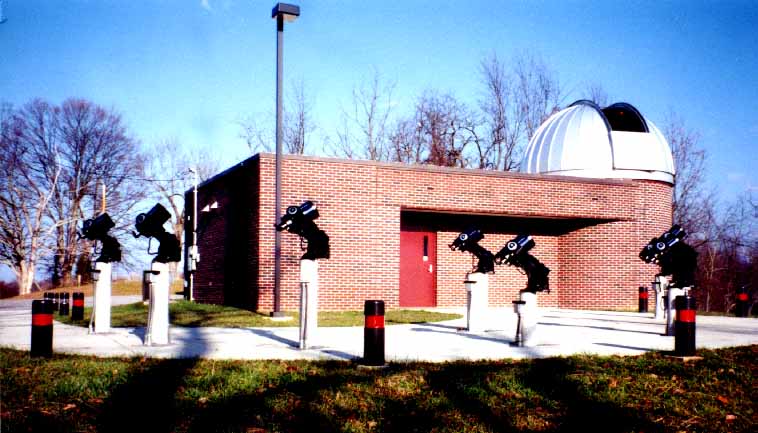

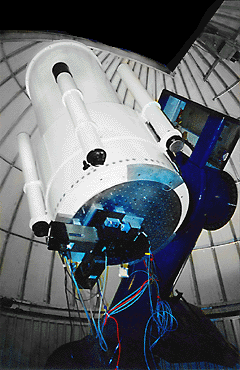
The ETSU Observatory, located on the hill behind campus. Under the dome is a 14 inch diameter Celestron telescope. The telescopes outside are 8 inch diameter Meade telescopes. These are all Cassegrain focus reflecting telescopes.

The
ETSU Observatory, located on the hill behind campus.
Under the dome is a 14 inch diameter Celestron telescope.
The telescopes outside are 8 inch diameter Meade telescopes.
These are all Cassegrain focus reflecting telescopes.
East Tennessee State University is one of
the five Universities
in the
Southeastern Association for
Research in Astronomy (SARA), which operates
this 0.9 meter (36 inch) telescope at Kitt Peak
in Arizona.
The SARA telescope is often operated
remotely from the eastern US.


Kitt Peak contains
a large number of telescopes,
in addition to the SARA telescope.
Most of these telescopes are operated
by the
National Optical Astronomical
Observatories (NOAO), a public facility for
professional astronomers from
all over the US.
The telescope shown on the right is the Kitt Peak
4m telescope.

This is the brand new 8.1m
Gemini
North
telescope built by the US (NOAO),
in collaboration with
the United Kingdom, Canada, Chile, Australia,
Argentina, and Brazil.
It is located on Mauna Kea, in Hawaii.
It was dedicated in June 1999, and
began general observations
in June 2000.
The matching Gemini South 8.1m telescope
is located on Cerro Pachon in central Chile.
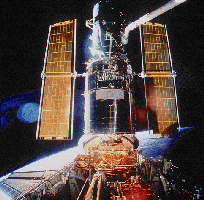
The
Hubble Space Telescope
has a 2.4 meter mirror, and
has instruments that operate at
ultraviolet,
optical,
and
infrared
wavelengths.

The
National
Radio Astronomy Observatory
100 meter telescope
was recently built in Green Bank, West Virginia.
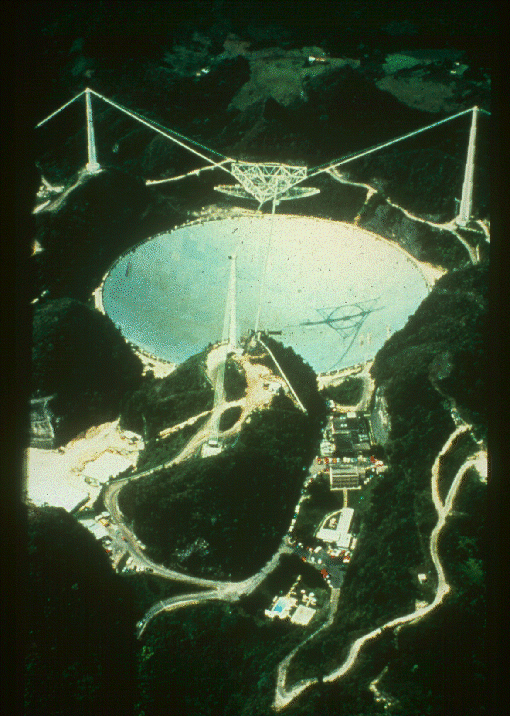
The 300 meter
Arecibo radio telescope,
in Puerto Rico.
It is built into a valley, and is not
steerable.

The
Very Large Array
in New Mexico:
a collection of 27 radio telescopes, each
with diameters of 25 meters,
covering up to 22 miles.
Working together, these provide very high resolution.

The
Kuiper Airborne Observatory.
A Lockheed C-141 aircraft which carried
a 0.9 meter optical/infrared telescope.
This observatory was run by NASA, and
operated from 1974 - 1995.

The
Stratospheric
Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA).
A planned 2.5 meter telescope to
be housed in a Boeing 747-SP aircraft.
This telescope will begin operations
in the year 2002. It is a collaborative project
between the US (NASA) and Germany.
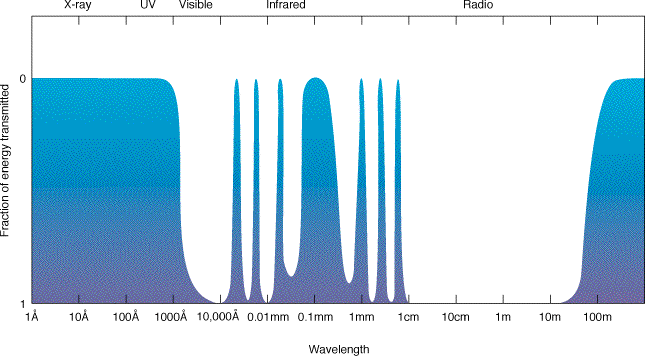
The transparency
of the Earth's atmosphere at different
wavelengths. In Gamma rays, X-rays, and ultraviolet,
nearly all the light is blocked by
the Earth's atmosphere. At only certain
infrared wavelengths does light get through
the Earth's atmosphere.
At radio waves, the atmosphere is transparent,
except at wavelengths longer than 100 meters.