
Mars is one of the seven objects visible to the naked eye which move relative to the (apparently) fixed stars (the other six being Mercury, Venus, Jupiter, Saturn, the Moon, and the Sun). Mars appears as a deep red "star" to the naked eye. This blood red color led the ancients to name this wandering star after the Roman god of war, Mars.
The first in-depth telesopic study of Mars came in the late 1800's. In 1877 the Italian astronomer Giovanni Schiaparelli announced that he had seen canali (the Italian word for "grooves") on Mars. This was translated into English as "canals" and caught the attention of the New England aristocrat Percival Lowell.

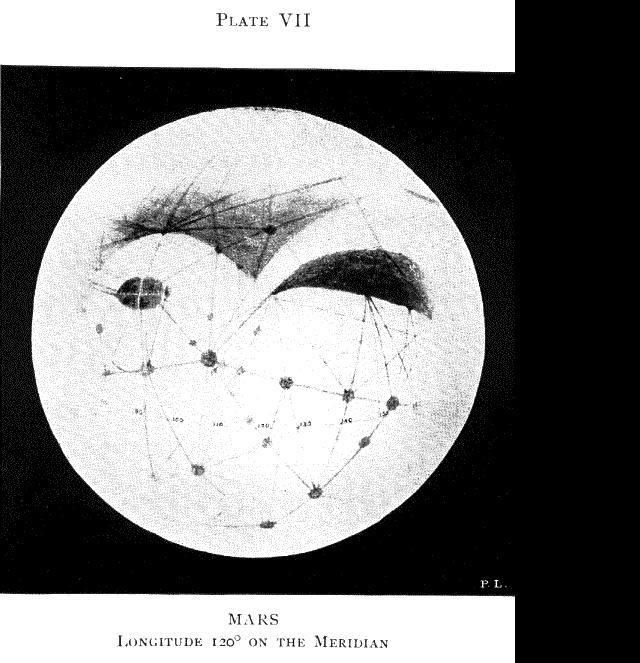
Telescopic studies of Mars continue even today. Unfortunately, the motions of the Earth and Mars around the Sun are such that Mars is close to Earth only once every two years or so. Fortunately, we will be in such a situation (called an opposition of Mars) this April.
