
The first U.S. spacecraft to visit Mars following the Viking missions, was planned to be the Mars Observer. It was to map Mars and monitor its atmosphere, to better help us understand Martian geology and climatology. Unfortunately, 3 days before entering orbit around Mars, the spacecraft fell silent. It is suspected that a mechanical failure with a rocket caused the Mars Observer to explode.
 |  |
The Mars Pathfinder landed on Mars on the 4th of July, 1997. The spacecraft consisted of two major parts: a lander equipped with cameras and meteorological instruments, and a robotic rover which contained a number of geologic instruments. The mission was primarily an engineering mission, demonstrating technologies and concepts for eventual use in future missions to Mars. Pathfinder studied the atmosphere, weather and geology of Mars.



The primary mission of the Mars Global Surveyor is the same as the ill-fated Mars Observer: to orbit Mars and study its atmosphere and climate for a full Martian year (687 Earth days). After completion of the mapping of the surface in January 2000, the spacecraft will function as a communication satellite to relay data back to Earth from surface landers launched as part of future Mars missions.
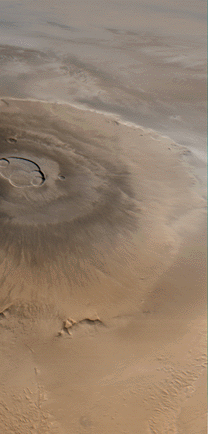 Olympus Mons, at a height of 16 miles, is taller than 3 Mount Everests and about as wide as the entire Hawaiian Island chain. This giant volcano is almost flat with its flanks sloping at 2o to 5o. The upper part of the volcano is rimmed with a band of whitish clouds. |
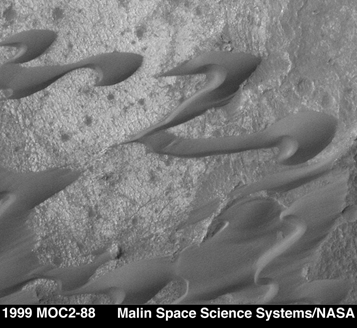
 A 310 km by 290 km view of a well developed dust storm covering the landing site of Viking 1 at Chryse Planitia. |