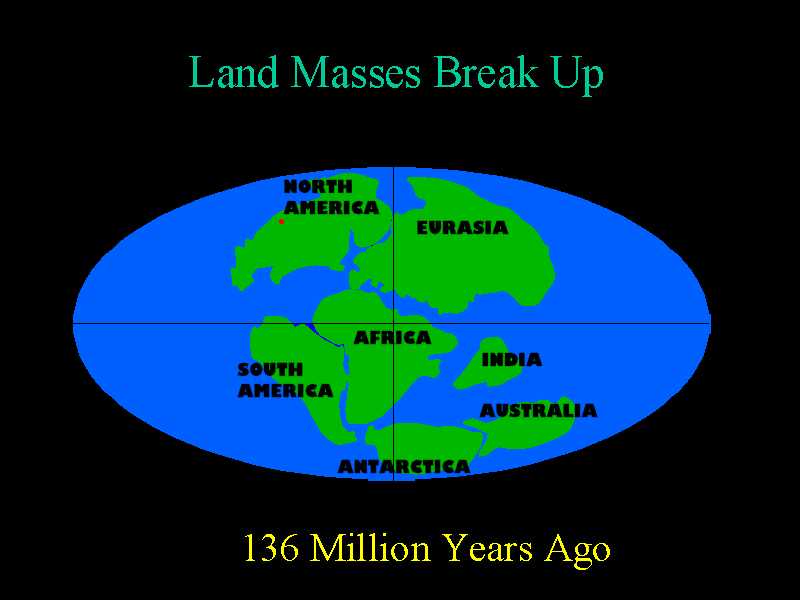
The Cretaceous Period lasted from 144 to 66 million years ago. Continental separation continued during the Cretaceous.

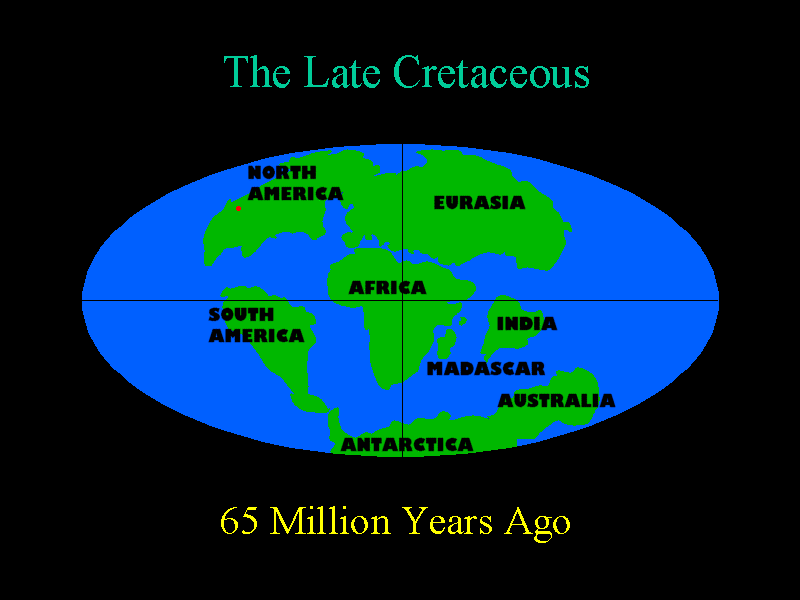
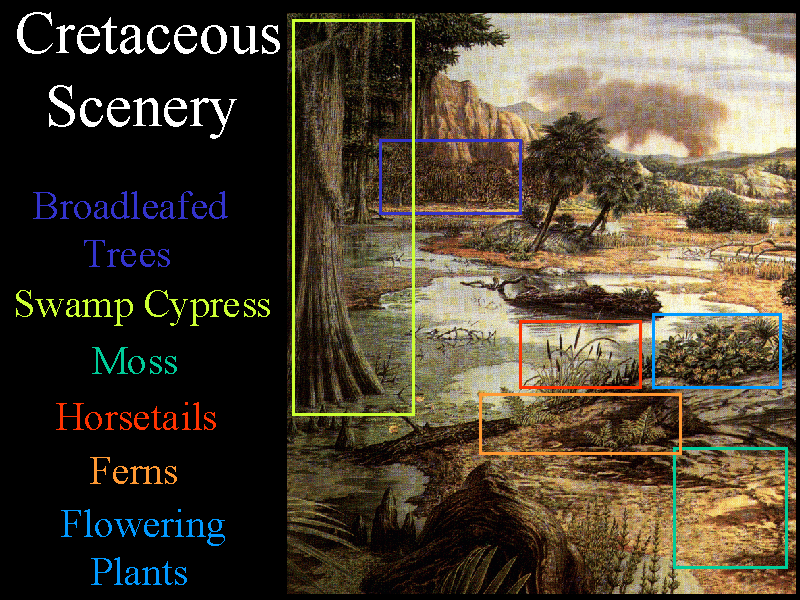
In the early Cretaceous, a progressive drying appears to have occurred. The equatorial regions were less heavily forested and may have developed into treeless savannahs with the ground covered by ferns and horsetails. The higher latitudes had forests of conifers, cycads, and ginkgos. In the Late Cretaceous the first flowering plants (the scientific name of which are angiosperms) appeared. Surprisingly, there were no grasses at any time of the dinosaurs. The ecological niches of grasses were filled by ferns which would have carpeted much of the moist areas of the Mesozoic.
Go to the next section.