Mars: A Century of Exploration
Life on Mars: The Science
Following the early theories of Martian life by Percival Lowell (which were
mostly discredited by the early 1900's), there was little progress until
the space age. With the first flyby and orbiter missions of the 1960's, it
became clear that, on the large scale, Mars was a desolate, cratered world.
In particular, with the negative results in the life experiments on the
Viking missions, the prospect for Martian life seemed grim.
Twenty years after the Viking missions, on August 7, 1996, a NASA team held
a press conference: they claimed to have tentative evidence of ancient
Martian microbes!
 The evidence concerned a meteorite found in the Allan
Hills region of Antartica (called ALH84001). Based on gases trapped in the
meteorite, it is almost universally agreed that the rock is from
Mars. It is also agreed that the potato sized object was formed 4.5
billion years ago as an igneous rock that crystallized slowly from molten
lava.
The evidence concerned a meteorite found in the Allan
Hills region of Antartica (called ALH84001). Based on gases trapped in the
meteorite, it is almost universally agreed that the rock is from
Mars. It is also agreed that the potato sized object was formed 4.5
billion years ago as an igneous rock that crystallized slowly from molten
lava.
 It was fractured and underwent chemical change while on Mars and was
ejected from Mars by an asteroid impact about 16 million years ago (based
on its exposure to cosmic rays in space),
fell in Antartica 13,000 years
ago (based on when cosmic ray exposure stopped), and was discovered in
1984. Whereas these claims are well accepted, the claim that the meteorite
holds fossilized Martians is not as widely accepted.
It was fractured and underwent chemical change while on Mars and was
ejected from Mars by an asteroid impact about 16 million years ago (based
on its exposure to cosmic rays in space),
fell in Antartica 13,000 years
ago (based on when cosmic ray exposure stopped), and was discovered in
1984. Whereas these claims are well accepted, the claim that the meteorite
holds fossilized Martians is not as widely accepted.
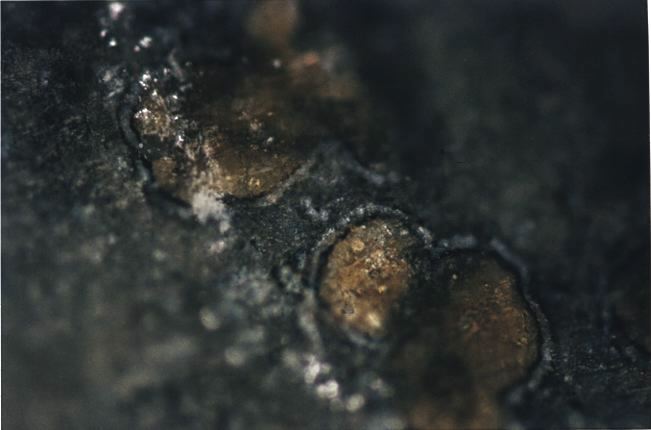 The rock contains tiny globules of carbonate minerals scattered along
fractures throughout it. The carbonates may have been deposited in the
cracks by Martian groundwater laden with carbon dioxide. All the evidence
for life is in the tiny carbonate globules and on their rims.
The team
reported four lines of evidence for ancient life:
The rock contains tiny globules of carbonate minerals scattered along
fractures throughout it. The carbonates may have been deposited in the
cracks by Martian groundwater laden with carbon dioxide. All the evidence
for life is in the tiny carbonate globules and on their rims.
The team
reported four lines of evidence for ancient life:
- carbon compunds suggestive of decayed organic matter,
- unusual, small crystals of magnetite (an iron oxide) matching identical
crystals that are made only by Earth bacteria,
- apparently incompatible minerals close together where proximity would
suggest organic action if the rock were from Earth, and
- bacteria-shaped formations detected in electron microscope
pictures.
After two years of investigation, some positions have changed. However,
there is still no final decision on whether the evidence is conclusive of
the presence of ancient Martian life.
It has been found that some of the compounds in the rock can be formed in
the absence of life (and at rather high temperatures for the presence of
life as we know it). There are concerns that some of the organic molecules
(PAHs - polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) might be the result of
contamination. However, the concentration of PAHs is greatest in the
center of the rock and least at the surface - the opposite of what would be
expected if the PAHs result from contamination.
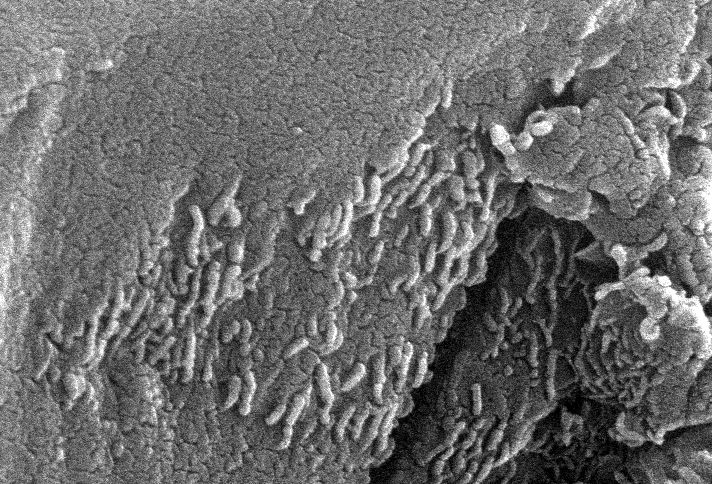 The most exciting signs of Martian life were electron microscope pictures
of bacteria-shaped objects (called BSOs). One original concern was that
the BSOs are about 2 to 10 times smaller than the smallest known
terrestrial bacteria (they were also called "nanobacteria"). The NASA team
has changed its position on the BSOs and now think they may be crystals of
magnetite or ridges on the mineral surface.
The most exciting signs of Martian life were electron microscope pictures
of bacteria-shaped objects (called BSOs). One original concern was that
the BSOs are about 2 to 10 times smaller than the smallest known
terrestrial bacteria (they were also called "nanobacteria"). The NASA team
has changed its position on the BSOs and now think they may be crystals of
magnetite or ridges on the mineral surface.
Despite some setbacks, the NASA team says the idea of Martian fossils in
ALH84001 is "still alive and kicking" and they are "more confident than
ever." Many critics remain and the scientific debate continues.
Go to
next section.




