Mars: A Century of Exploration
Mars: The Specs
 When comparing Mars with Earth, we first notice that it is about half the
diameter of our home planet. Here are several of the physical parameters
for Mars and Earth.
When comparing Mars with Earth, we first notice that it is about half the
diameter of our home planet. Here are several of the physical parameters
for Mars and Earth.
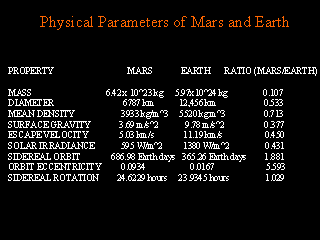 If we are interested in visiting Mars
and returning, then the numbers presented here that are of primary concern
are surface gravity, orbital period and rotational period. The force of
gravity at the surface of Mars is about 40% of that at the surface of the
Earth. This means that it will take much less energy to launch astronauts
from the surface of Mars than from the surface of Earth. We have already
mentioned that the orbital periods of Earth and Mars imply that the two
planets are "close together" only every two years. Finally, an
interesting coincidence is that the rotational periods of Earth and Mars
differ by only about 3%, meaning that a Martian day is about 42 minutes
longer than an Earth day.
If we are interested in visiting Mars
and returning, then the numbers presented here that are of primary concern
are surface gravity, orbital period and rotational period. The force of
gravity at the surface of Mars is about 40% of that at the surface of the
Earth. This means that it will take much less energy to launch astronauts
from the surface of Mars than from the surface of Earth. We have already
mentioned that the orbital periods of Earth and Mars imply that the two
planets are "close together" only every two years. Finally, an
interesting coincidence is that the rotational periods of Earth and Mars
differ by only about 3%, meaning that a Martian day is about 42 minutes
longer than an Earth day.
 The average surface
air pressure on Mars is only about 0.6% of the average surface pressure on
Earth. The average surface temperature on Mars is about equal to the
coldest temperatures ever recorded on the surface of the Erath. Also, the
molecular composition of the Martian atmosphere is quite different from
that on Earth. These three properties imply that astronauts on mars will
need heated, pressurized suits with onboard oxygen supplies.
The average surface
air pressure on Mars is only about 0.6% of the average surface pressure on
Earth. The average surface temperature on Mars is about equal to the
coldest temperatures ever recorded on the surface of the Erath. Also, the
molecular composition of the Martian atmosphere is quite different from
that on Earth. These three properties imply that astronauts on mars will
need heated, pressurized suits with onboard oxygen supplies.
Go to
next section.



