
An optical image of the spiral galaxy NGC 891. This galaxy, seen from the side, may resemble the Milky Way. Notice the dust lane in the disk.

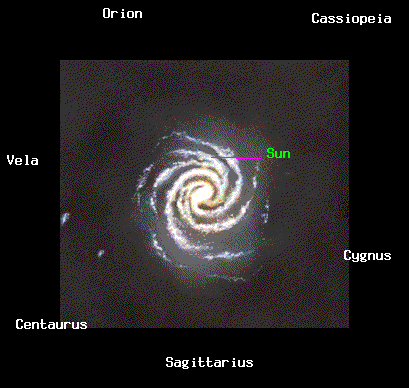

The Sombrero galaxy (M104), a
spiral galaxy with a large bulge, seen edge-on.
Image
from the
Anglo-Australian Observatory.
Copyright Anglo-Australian
Observatory.

M100, a face-on
galaxy.
Image
from the
Anglo-Australian Observatory.
Copyright Anglo-Australian
Observatory.

The Andromeda galaxy
(M31), the closest large spiral to the Milky Way.
The two companion galaxies
are M32 and NGC 205, two dwarf elliptical
galaxies. M32 is the closer galaxy to M31.
Images
from the
Messier Catalog
web page.

The barred spiral galaxy,
NGC 2442.
Image
from the
Anglo-Australian Observatory.
Copyright Anglo-Australian
Observatory.
ELLIPTICAL GALAXIES

The giant elliptical M87.
Image
from the
Anglo-Australian Observatory.
Copyright Anglo-Australian
Observatory.

Dwarf elliptical galaxies near the
spiral galaxy M100.
Image
from the
Anglo-Australian Observatory.
Copyright Anglo-Australian
Observatory.
IRREGULAR GALAXIES

The Large Magellanic Cloud.
Image
from the
Anglo-Australian Observatory.
Copyright Anglo-Australian
Observatory/Royal Observatory, Edinburgh.

The Small Magellanic Cloud.
Image
from the
Anglo-Australian Observatory.
Copyright Anglo-Australian
Observatory/Royal Observatory, Edinburgh.
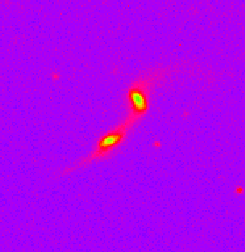

Left: IRAS 03119+1448.
Right: Arp 295.
(IRAS 03119+1448
image from
Beverly Smith
at East Tennessee State University.)
Arp 295 image from
John Hibbard at the
National Radio Astronomy Observatory.)
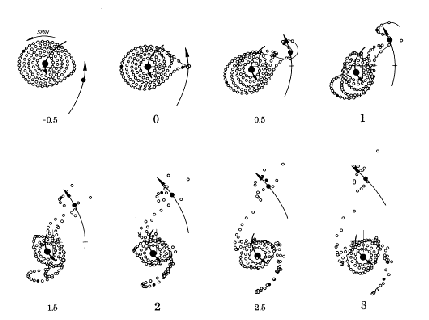
Left: A simulation by the Toomres of
a low mass companion passing
close to a disk galaxy.
Right: An optical
image of Arp 82, an interacting
pair of galaxies.
(Image from
Beverly Smith
at East Tennessee State University.)
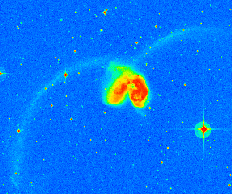

Left: an optical image
of the Antennae galaxies (NGC 4038/9).
Right: a computer model of the Antennae
galaxies by the Toomres.
Image from the
Digitized Sky Survey.
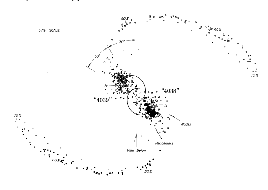
The same model of the Antennae pair,
seen from a different direction.
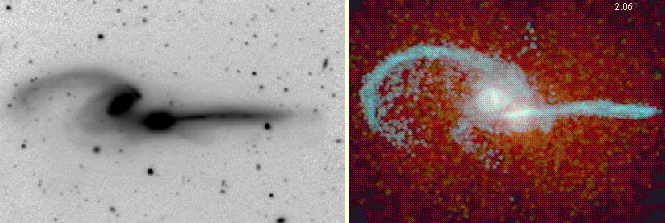
The Mice (NGC 4676).
Left: An optical image.
right: A computer model.
(Image from
John Hibbard at the National Radio Observatory.
Model from
John Hibbard at the National Radio Observatory
and
Josh Barnes
at the Institute for Astronomy.)
Click
here to see a simulation
of this interaction.
Click
here to rotate the
model, to see the three dimensional structure.
(These movies are from
John Hibbard at the National Radio Observatory
and
Josh Barnes
at the Institute for Astronomy.)
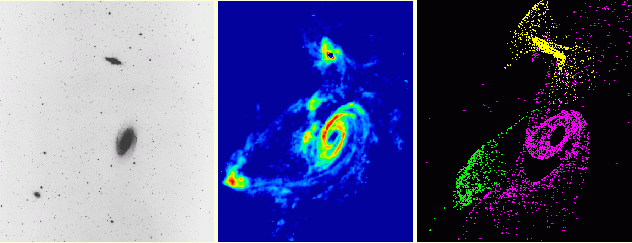
Left: An optical image of
the M81/M82/NGC 3077 group. M81 is the brightest
galaxy, M82 is at the top of the image,
and NGC 3077 is to the right.
Middle: A 21 cm HI map of the same region.
Note that the three galaxies are connected
by bridges.
Right: A computer model of this system.
(These images are from
Min Yun at the
National Radio Astronomy Observatory)
Click here to see a movie of this interaction. (movie from Min Yun at the National Radio Astronomy Observatory)
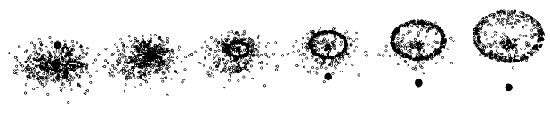
A model illustrating ring formation.
(model by A. Toomre)

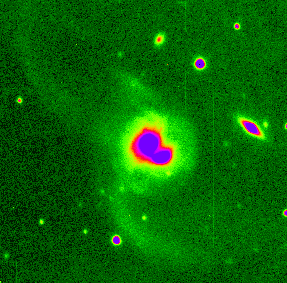
A
Hubble Space Telescope
image of
the interacting galaxy pair NGC 7714/5.
Notice the partial ring and the bridge connecting the two galaxies.
Also notice the young clusters of stars in the bridge.
(Images from
Beverly Smith
at East Tennessee State University.)
Click here to see a computer model of this encounter. (Movie from Beverly Smith at East Tennessee State University.)
Click here to see a simulation of two disk galaxies merging. Movie from Chris Mihos at Case Western Reserve University.
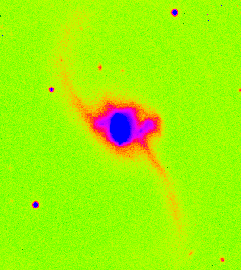
Left: NGC 6090, two spirals
in the process of merging. Note that there are still
two disks.
Right: NGC 2623, a merging pair of galaxies:
only one body is evident.
(Images from
Beverly Smith
at East Tennessee State University.)

Centaurus A, a peculiar elliptical.
This may have merged with a spiral galaxy.
Image
from the
Anglo-Australian Observatory.
Copyright Anglo-Australian
Observatory.
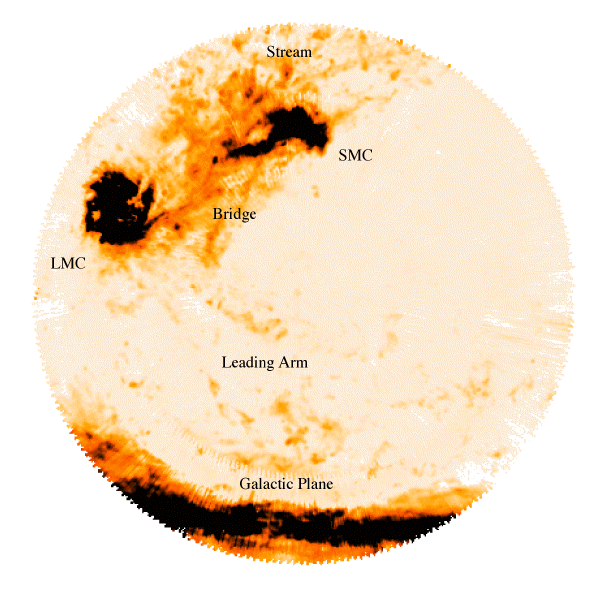
An HI map of the region
near the LMC and SMC.
Data obtained by
Mary Putnam
and her collaborators using the
Australian Telescope National
Facility.
Click here to see a computer model showing the merger of a low mass companion with a disk galaxy. (Movie from Chris Mihos at Case Western Reserve University.)
