


Next: Problems
Up: Chapter 03
Previous: Chapter 03
- #01
- An undulation that transports energy from one place to another.
- #02
- A wave is a repetitious pattern that moves. Period is the time
taken for a feature of the pattern to repeat as the wave moves past a point.
Wavelength is the distance between said feature and the next occurrence of
that feature (e.g., from peak to peak, or trough to trough). Amplitude
is the size of the wave, which is a measure of the energy transported.
Frequency is 1/period, or the number of cycles of the repeating pattern
that passes a point every second.
- #03
- For wavelength
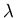 , frequency
, frequency 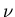 , and wave speed
, and wave speed 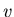 ,
these are related by
,
these are related by
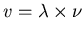 .
.
- #11
- They are all forms of electromagnetic waves.
They all travel at the speed of light
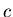 in vacuum. However, they
are different in wavelength, frequency, and energy.
in vacuum. However, they
are different in wavelength, frequency, and energy.
- #13
- Blackbodies are objects that absorb all light falling upon
them. They are however not black holes nor even black. They glow,
in such as way as to emit radiation in every wave band or color (i.e.,
at every wavelength and frequency), but not equally so. Thus
a blackbody produces a continuous spectrum. The band in
which they emit peak radiation is determined by the object's temperature.
- #14
- They have different temperatures.
- #15
- All else being equal, hotter blackbodies emit much more
radiation than cooler ones (in a per unit area sense).
- #17
- The Doppler effect refers to how wavelengths and frequencies
change when an emitter and receiver experience a relative motion between
one another. When moving together, wavelength is shortened and frequency
increased. When separating, the opposite results.



Next: Problems
Up: Chapter 03
Previous: Chapter 03
Rico Ignace
2004-09-10